Secure your systems by arming yourself with knowledge

Network is where at least two nodes/hosts (laptops, desktops, mainframes, cellphones, …etc.) are communicating with each other. In a communication session, one host acts as a client (requesting information) and one acts as a server (providing information). When networks were first developed, a host either acted as a client or server at one time. Fortunately for us, scientists and engineers figured out how to improve communication by allowing devices to be both clients and servers simultaneously.
Types of Networks!
The internet is interconnection of networks. When you connect to the internet, the internet connects to you. There are two types of networks that makes up most the internet, Local Area Networks(LANS) and Wide Area Networks(WANS). The size of a network, i.e. the number of hosts in the network, doesn’t determine if it’s a LAN or WAN. It’s how the hosts connect and their geographic location that makes that determination. Most end users connect to a LAN, and LANs connect to each other through WANs. For example, when a small business owner downloads a file from their server, they have successfully connected to the office LAN. When the owner is home, and on their network-enabled printer, prints a file from a USB flash drive on their laptop; they were connected to their home LAN. Lastly, if the owner needed a file on the office’s network share, quickly and securely; they would log in to their company’s network via a VPN connection and retrieve the file. Because these two areas are most likely separate in geographic location; the owner needs to rely on their ISP(s) for a WAN connection.
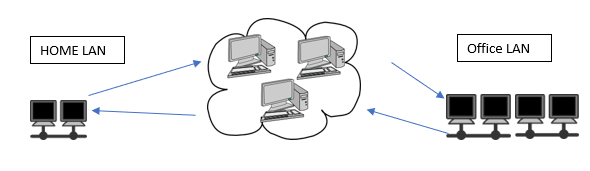 How do computers communicate with each other over a network?
How do computers communicate with each other over a network?
Communication between computers go through a similar process as humans. Both humans and computers require several sequential processes to communicate efficiently. For example, when humans communicate (taking into consideration all mental faculties and senses are working), one person is talking while the other person is listening. The client in this example would be the one talking. His/her brain gathers their thoughts, then the brain sends the message to the mouth and the person begins to speak. The receiving individual intercepts the message, the ears send the message to the brain and the brain processes the information it just received.
For computer networks, scientists created a layered approach to ensure reliable communication. It is called the TCP/IP model, and there are different versions to this model. However, for the purposes of this article we will refer to the Kurose, Forouzan model. The Application layer helps categorizes the data that will enter and leave the network. All layers contain protocols(instructions), and the protocols in layer one instructs how to categorize data; with web pages, emails and file transfer being the most popular categories. It’s also responsible for translating and preparing the data for the transport layer.
Some categories of data need more reliable consistent connection while others just need to reach their destination. The Second layer, the Transport layer, takes that responsibility. Its protocols determine how the different type of data will traverse the network. The Network later, appropriately named, has protocols that utilize pre-existing networks to determine the route required for data travel. Just as we use our mailing address to identify our location on the globe. Computers use a network identifier called an IP address to determine our exit off the WAN highway.
The next layer, the Link layer, determines what type of network technology is being used. LAN or WAN, Ethernet or Wi-Fi, they each have their own way of communicating. There are devices called gateways, that support multiple technologies and act as a translator. The Link layer is responsible for converting bits of data into electrical signals or light particles. Which the final layer, the Physical layer uses to transmit the data to its next immediate physical stop. In summary, as data leaves a computer, it traverses through all the layers and enters a communication medium (wire and/or wireless) to reach its destination. The receiving computer picks up the data and It travels the same layers but in reverse order, eventually reaching the end user. There are intermediary computers, that only read data in the Link and/or Network layer, to expedite processing and forwarding.
Advantages and Disadvantages!
The ideal for any end-user should be to connect to an optimized and secure network. Networks, following a layered model has its benefits and its flaws. Having devices and protocols operating in specific layers, speeds up the communication process. The same principal applies for executives of a company. I’m sure a CEO can be the visionary, run operations, handle the technical infrastructure, and monitor the financials. However, the job is much easier with a Chief Financial Officer, Chief Operations Officer and a Chief Technology Officer.
Unfortunately, networks being systemized, means they are prone to manipulation, aka Hacking. Taking control of a layer can effectively control the system, once communication between layers is interrupted. If your competitor corrupts your CTO, who convinces your CFO to over report earnings and your COO to gnore something that needs attention; your company has been hacked. So, the lesson learned here, is to prevent such atrocities from occurring and/or mitigate damage if preventative measures fail.
Conclusion
This article is for the end-user wondering if their data is protected, and/or the pc technician with budding interest in the world of networking. By understanding what a network is and how it works, you are better prepared to secure it. Unfortunately, systems are compromised daily, from the residential end user’s PC to the largest financial institutions’ servers. Brilliant computer scientists with malicious agendas, are the major culprits. Some do it for the money, others do it for pride and others do it because they are bored. Whatever the reason is, the reality is they cannot be stopped only deterred. However, there is no reason to fear; you expect it to rain you carry an umbrella. Whether it rains or not, you have peace of mind. If you are hacked, and the worst they can do is merely inconvenience you, you have prepared well. So how do you secure your data? By using security applications and hardware that operates on the different layers and by periodically backing up your data. You can find out more, in my next article.
Omar Claxton
Posted in S.T.E.A.M.  Network is where at least two nodes/hosts (laptops, desktops, mainframes, cellphones, …etc.) are communicating with each other. In a communication session, one host acts as a client (requesting information) and one acts as a server (providing information). When networks were first developed, a host either acted as a client or server at one time. Fortunately for us, scientists and engineers figured out how to improve communication by allowing devices to be both clients and servers simultaneously.
Types of Networks!
The internet is interconnection of networks. When you connect to the internet, the internet connects to you. There are two types of networks that makes up most the internet, Local Area Networks(LANS) and Wide Area Networks(WANS). The size of a network, i.e. the number of hosts in the network, doesn’t determine if it’s a LAN or WAN. It’s how the hosts connect and their geographic location that makes that determination. Most end users connect to a LAN, and LANs connect to each other through WANs. For example, when a small business owner downloads a file from their server, they have successfully connected to the office LAN. When the owner is home, and on their network-enabled printer, prints a file from a USB flash drive on their laptop; they were connected to their home LAN. Lastly, if the owner needed a file on the office’s network share, quickly and securely; they would log in to their company’s network via a VPN connection and retrieve the file. Because these two areas are most likely separate in geographic location; the owner needs to rely on their ISP(s) for a WAN connection.
Network is where at least two nodes/hosts (laptops, desktops, mainframes, cellphones, …etc.) are communicating with each other. In a communication session, one host acts as a client (requesting information) and one acts as a server (providing information). When networks were first developed, a host either acted as a client or server at one time. Fortunately for us, scientists and engineers figured out how to improve communication by allowing devices to be both clients and servers simultaneously.
Types of Networks!
The internet is interconnection of networks. When you connect to the internet, the internet connects to you. There are two types of networks that makes up most the internet, Local Area Networks(LANS) and Wide Area Networks(WANS). The size of a network, i.e. the number of hosts in the network, doesn’t determine if it’s a LAN or WAN. It’s how the hosts connect and their geographic location that makes that determination. Most end users connect to a LAN, and LANs connect to each other through WANs. For example, when a small business owner downloads a file from their server, they have successfully connected to the office LAN. When the owner is home, and on their network-enabled printer, prints a file from a USB flash drive on their laptop; they were connected to their home LAN. Lastly, if the owner needed a file on the office’s network share, quickly and securely; they would log in to their company’s network via a VPN connection and retrieve the file. Because these two areas are most likely separate in geographic location; the owner needs to rely on their ISP(s) for a WAN connection.
 How do computers communicate with each other over a network?
Communication between computers go through a similar process as humans. Both humans and computers require several sequential processes to communicate efficiently. For example, when humans communicate (taking into consideration all mental faculties and senses are working), one person is talking while the other person is listening. The client in this example would be the one talking. His/her brain gathers their thoughts, then the brain sends the message to the mouth and the person begins to speak. The receiving individual intercepts the message, the ears send the message to the brain and the brain processes the information it just received.
For computer networks, scientists created a layered approach to ensure reliable communication. It is called the TCP/IP model, and there are different versions to this model. However, for the purposes of this article we will refer to the Kurose, Forouzan model. The Application layer helps categorizes the data that will enter and leave the network. All layers contain protocols(instructions), and the protocols in layer one instructs how to categorize data; with web pages, emails and file transfer being the most popular categories. It’s also responsible for translating and preparing the data for the transport layer.
Some categories of data need more reliable consistent connection while others just need to reach their destination. The Second layer, the Transport layer, takes that responsibility. Its protocols determine how the different type of data will traverse the network. The Network later, appropriately named, has protocols that utilize pre-existing networks to determine the route required for data travel. Just as we use our mailing address to identify our location on the globe. Computers use a network identifier called an IP address to determine our exit off the WAN highway.
How do computers communicate with each other over a network?
Communication between computers go through a similar process as humans. Both humans and computers require several sequential processes to communicate efficiently. For example, when humans communicate (taking into consideration all mental faculties and senses are working), one person is talking while the other person is listening. The client in this example would be the one talking. His/her brain gathers their thoughts, then the brain sends the message to the mouth and the person begins to speak. The receiving individual intercepts the message, the ears send the message to the brain and the brain processes the information it just received.
For computer networks, scientists created a layered approach to ensure reliable communication. It is called the TCP/IP model, and there are different versions to this model. However, for the purposes of this article we will refer to the Kurose, Forouzan model. The Application layer helps categorizes the data that will enter and leave the network. All layers contain protocols(instructions), and the protocols in layer one instructs how to categorize data; with web pages, emails and file transfer being the most popular categories. It’s also responsible for translating and preparing the data for the transport layer.
Some categories of data need more reliable consistent connection while others just need to reach their destination. The Second layer, the Transport layer, takes that responsibility. Its protocols determine how the different type of data will traverse the network. The Network later, appropriately named, has protocols that utilize pre-existing networks to determine the route required for data travel. Just as we use our mailing address to identify our location on the globe. Computers use a network identifier called an IP address to determine our exit off the WAN highway.
 The next layer, the Link layer, determines what type of network technology is being used. LAN or WAN, Ethernet or Wi-Fi, they each have their own way of communicating. There are devices called gateways, that support multiple technologies and act as a translator. The Link layer is responsible for converting bits of data into electrical signals or light particles. Which the final layer, the Physical layer uses to transmit the data to its next immediate physical stop. In summary, as data leaves a computer, it traverses through all the layers and enters a communication medium (wire and/or wireless) to reach its destination. The receiving computer picks up the data and It travels the same layers but in reverse order, eventually reaching the end user. There are intermediary computers, that only read data in the Link and/or Network layer, to expedite processing and forwarding.
Advantages and Disadvantages!
The ideal for any end-user should be to connect to an optimized and secure network. Networks, following a layered model has its benefits and its flaws. Having devices and protocols operating in specific layers, speeds up the communication process. The same principal applies for executives of a company. I’m sure a CEO can be the visionary, run operations, handle the technical infrastructure, and monitor the financials. However, the job is much easier with a Chief Financial Officer, Chief Operations Officer and a Chief Technology Officer.
Unfortunately, networks being systemized, means they are prone to manipulation, aka Hacking. Taking control of a layer can effectively control the system, once communication between layers is interrupted. If your competitor corrupts your CTO, who convinces your CFO to over report earnings and your COO to gnore something that needs attention; your company has been hacked. So, the lesson learned here, is to prevent such atrocities from occurring and/or mitigate damage if preventative measures fail.
Conclusion
This article is for the end-user wondering if their data is protected, and/or the pc technician with budding interest in the world of networking. By understanding what a network is and how it works, you are better prepared to secure it. Unfortunately, systems are compromised daily, from the residential end user’s PC to the largest financial institutions’ servers. Brilliant computer scientists with malicious agendas, are the major culprits. Some do it for the money, others do it for pride and others do it because they are bored. Whatever the reason is, the reality is they cannot be stopped only deterred. However, there is no reason to fear; you expect it to rain you carry an umbrella. Whether it rains or not, you have peace of mind. If you are hacked, and the worst they can do is merely inconvenience you, you have prepared well. So how do you secure your data? By using security applications and hardware that operates on the different layers and by periodically backing up your data. You can find out more, in my next article.
Omar ClaxtonPosted in S.T.E.A.M.
The next layer, the Link layer, determines what type of network technology is being used. LAN or WAN, Ethernet or Wi-Fi, they each have their own way of communicating. There are devices called gateways, that support multiple technologies and act as a translator. The Link layer is responsible for converting bits of data into electrical signals or light particles. Which the final layer, the Physical layer uses to transmit the data to its next immediate physical stop. In summary, as data leaves a computer, it traverses through all the layers and enters a communication medium (wire and/or wireless) to reach its destination. The receiving computer picks up the data and It travels the same layers but in reverse order, eventually reaching the end user. There are intermediary computers, that only read data in the Link and/or Network layer, to expedite processing and forwarding.
Advantages and Disadvantages!
The ideal for any end-user should be to connect to an optimized and secure network. Networks, following a layered model has its benefits and its flaws. Having devices and protocols operating in specific layers, speeds up the communication process. The same principal applies for executives of a company. I’m sure a CEO can be the visionary, run operations, handle the technical infrastructure, and monitor the financials. However, the job is much easier with a Chief Financial Officer, Chief Operations Officer and a Chief Technology Officer.
Unfortunately, networks being systemized, means they are prone to manipulation, aka Hacking. Taking control of a layer can effectively control the system, once communication between layers is interrupted. If your competitor corrupts your CTO, who convinces your CFO to over report earnings and your COO to gnore something that needs attention; your company has been hacked. So, the lesson learned here, is to prevent such atrocities from occurring and/or mitigate damage if preventative measures fail.
Conclusion
This article is for the end-user wondering if their data is protected, and/or the pc technician with budding interest in the world of networking. By understanding what a network is and how it works, you are better prepared to secure it. Unfortunately, systems are compromised daily, from the residential end user’s PC to the largest financial institutions’ servers. Brilliant computer scientists with malicious agendas, are the major culprits. Some do it for the money, others do it for pride and others do it because they are bored. Whatever the reason is, the reality is they cannot be stopped only deterred. However, there is no reason to fear; you expect it to rain you carry an umbrella. Whether it rains or not, you have peace of mind. If you are hacked, and the worst they can do is merely inconvenience you, you have prepared well. So how do you secure your data? By using security applications and hardware that operates on the different layers and by periodically backing up your data. You can find out more, in my next article.
Omar ClaxtonPosted in S.T.E.A.M.